上一章节中(Android让Fragment加载到Activity中),我们对Fragment的生命周期进行了简单介绍,这一章节将对生命周期和返回栈进行详细介绍。
一、Fragment的生命周期初探:
因为Fragment必须嵌入在Acitivity中使用,所以Fragment的生命周期和它所在的Activity是密切相关的。
假如Activity是暂停状态,其中所有的Fragment都是暂停状态;假如Activity是stopped状态,这个Activity中所有的Fragment都不能被启动;假如Activity被销毁,那么它其中的所有Fragment都会被销毁。
但是,当Activity在活动状态,可以独立控制Fragment的状态,比如加上或者移除Fragment。
当这样进行fragment transaction(转换)的时候,可以把fragment放入Activity的back stack中,这样用户就可以进行返回操作。
使用Fragment时,需要继承Fragment或者Fragment的子类(DialogFragment, ListFragment, PreferenceFragment, WebViewFragment),所以Fragment的代码看起来和Activity的类似。
每当创建一个Fragment时,首先添加以下三个回调方法:
onCreate():系统在创建Fragment的时候调用这个方法,这里应该初始化相关的组件,一些即便是被暂停或者被停止时依然需要保留的东西。 onCreateView():当第一次绘制Fragment的UI时系统调用这个方法,该方法将返回一个View,假如Fragment不提供UI也可以返回null。注意,假如继承自ListFragment,onCreateView()默认的实现会返回一个ListView,所以不用自己实现。 onPause():当用户离开Fragment时第一个调用这个方法,需要提交一些变化,因为用户很可能不再返回来。将Fragment加载到Activity当中有两种方式:
方式一:添加Fragment到Activity的布局文件当中 方式二:在Activity的代码中动态添加Fragment(荐)第一种方式虽然简单但灵活性不够。添加Fragment到Activity的布局文件当中,就等同于将Fragment及其视图与activity的视图绑定在一起,且在activity的生命周期过程中,无法切换fragment视图。
第二种方式比较复杂,但也是唯一一种可以在运行时控制fragment的方式(加载、移除、替换)。
二、Fragment的生命周期详解:
先来看一下官方文档的图片吧:
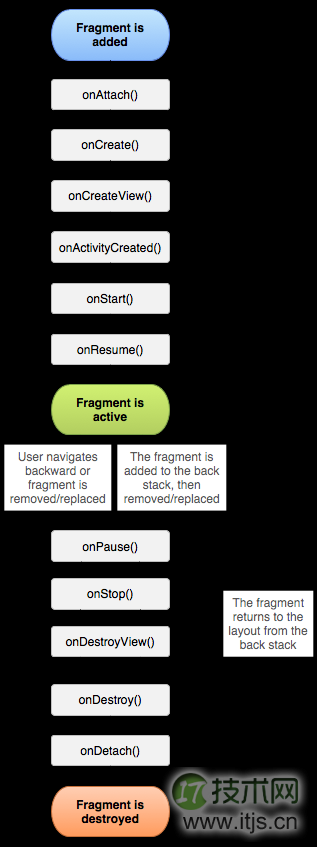
我们再把Activity的生命周期和Fragment的生命周期对比一下,就清楚很多了:
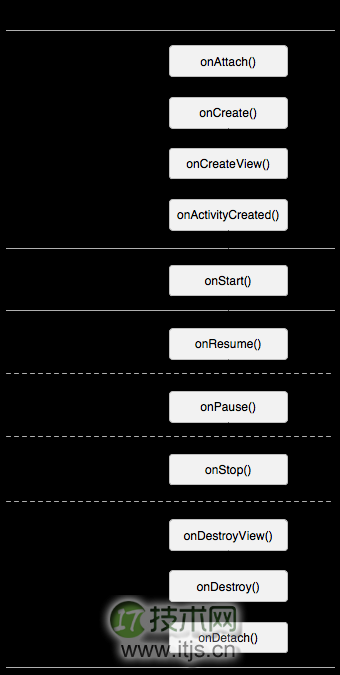
我们还是在实例中来看一下Fragment的生命周期吧。
【实例】在MainActivity中加载一个Fragment:(完整版代码如下)
我们所创建的Fragment的布局文件fragment01.xml的代码如下:
< xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" >
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<RatingBar
android:id="@+id/ratingBar1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button" />
</LinearLayout>
MyFragment.java代码如下:(注意生命周期中每个方法的作用)
1 package com.example.m01_fragmentlifecycle;
2
3 import android.app.Activity;
4 import android.app.Fragment;
5 import android.os.Bundle;
6 import android.util.Log;
7 import android.view.LayoutInflater;
8 import android.view.View;
9 import android.view.ViewGroup;
10
11 public class MyFragment extends Fragment {
12 private final String TAG = "MyFragment";
13
14 //获得activity的传递的值
15 @Override
16 public void onAttach(Activity activity) {
17 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
18 super.onAttach(activity);
19 Log.i(TAG, "--MyFragment->>onAttach");
20 }
21
22 //实例化成员变量
23 @Override
24 public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
25 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
26 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
27 Log.i(TAG, "--MyFragment->>onCreate");
28 }
29
30 //给当前的fragment绘制UI布局,可以使用线程更新UI
31 @Override
32 public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
33 Bundle savedInstanceState) {
34 Log.i(TAG, "--MyFragment->>onCreateView");
35 View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment01, null);
36 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
37 return view;
38 }
39
40 //表示activity执行oncreate方法完成了的时候会调用此方法
41 @Override
42 public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
43 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
44 super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
45 Log.i(TAG, "--MyFragment->>onActivityCreated");
46 }
47
48 //和activity一致
49 @Override
50 public void onStart() {
51 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
52 super.onStart();
53 Log.i(TAG, "--MyFragment->>onStart");
54 }
55
56 //和activity一致
57 @Override
58 public void onResume() {
59 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
60 super.onResume();
61 Log.i(TAG, "--MyFragment->>onResume");
62 }
63
64 //和activity一致
65 @Override
66 public void onPause() {
67 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
68 super.onPause();
69 Log.i(TAG, "--MyFragment->>onPause");
70 }
71
72 //和activity一致
73 @Override
74 public void onStop() {
75 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
76 super.onStop();
77 Log.i(TAG, "--MyFragment->>onStop");
78 }
79
80 //表示fragment销毁相关联的UI布局
81 @Override
82 public void onDestroyView() {
83 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
84 super.onDestroyView();
85 Log.i(TAG, "--MyFragment->>onDestroyView");
86 }
87
88 //销毁fragment对象
89 @Override
90 public void onDestroy() {
91 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
92 super.onDestroy();
93 Log.i(TAG, "--MyFragment->>onDestroy");
94 }
95
96 //脱离activity
97 @Override
98 public void onDetach() {
99 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
100 super.onDetach();
101 Log.i(TAG, "--MyFragment->>onDetach");
102 }
103 }
activity_main.xml的代码如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/line"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
MainActivity.java的代码如下:
1 package com.example.m01_fragmentlifecycle;
2
3 import android.os.Bundle;
4 import android.app.Activity;
5 import android.app.FragmentManager;
6 import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
7 import android.util.Log;
8 import android.view.Menu;
9
10 public class MainActivity extends Activity {
11 private final String TAG = "MainActivity";
12 private FragmentManager manager;
13 private FragmentTransaction transaction;
14
15 @Override
16 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
17 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
18 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
19 manager = getFragmentManager();
20 transaction = manager.beginTransaction();
21 MyFragment fragment = new MyFragment();
22 transaction.add(R.id.line, fragment);
23 transaction.commit();
24 Log.i(TAG, "--MainActivity->>onCreate");
25 }
26
27 @Override
28 protected void onStart() {
29 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
30 super.onStart();
31 Log.i(TAG, "--MainActivity->>onStart");
32 }
33
34 @Override
35 protected void onResume() {
36 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
37 super.onResume();
38 Log.i(TAG, "--MainActivity->>onResume");
39 }
40
41 @Override
42 protected void onPause() {
43 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
44 super.onPause();
45 Log.i(TAG, "--MainActivity->>onPause");
46 }
47
48 @Override
49 protected void onStop() {
50 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
51 super.onStop();
52 Log.i(TAG, "--MainActivity->>onStop");
53 }
54
55 @Override
56 protected void onRestart() {
57 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
58 super.onRestart();
59 Log.i(TAG, "--MainActivity->>onRestart");
60 }
61 @Override
62 protected void onDestroy() {
63 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
64 super.onDestroy();
65 Log.i(TAG, "--MainActivity->>onDestroy");
66 }
67
68 @Override
69 public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
70 // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
71 getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
72 return true;
73 }
74 }
可以看到,上面的代码在每个生命周期的方法里都打印了日志,然后我们来运行一下程序,可以看到打印日志如下:
初次加载:(分成两部分来看)
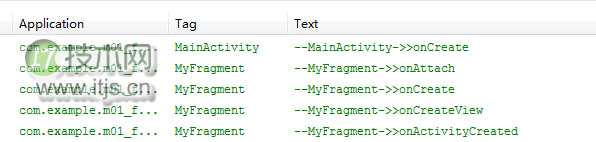

点击一下home键(或接入电话),打印日志如下:
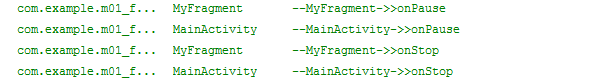
重新进入进入程序(或电话结束),打印日志如下:

点击back键退出程序,打印日志如下:

通过上面的日志,我们能够看出,Fragment和Activity的生命周期太相似了。只是有几个Activity中没有的新方法,需要重点介绍一下:
onAttach方法:Fragment和Activity建立关联的时候调用(获得activity的传递的值) onCreateView方法:为Fragment创建视图(加载布局)时调用(给当前的fragment绘制UI布局,可以使用线程更新UI) onActivityCreated方法:当Activity中的onCreate方法执行完后调用(表示activity执行oncreate方法完成了的时候会调用此方法) onDestroyView方法:Fragment中的布局被移除时调用(表示fragment销毁相关联的UI布局) onDetach方法:Fragment和Activity解除关联的时候调用(脱离activity)三、Fragment返回栈的管理:
将Fragment添加到返回栈中:
假设现在我们有两个Fragment:Fragment01和Fragment02,我们现在从Fragment01的界面跳到Fragment02,然后按Back键,发现程序是直接退出了,而不是返回到Fragment01。假如现在想实现以下功能:从Fragment01的界面跳到Fragment02,然后按Back键,会返回到Fragment01。这个功能该怎么实现呢?这其实就利用到了返回栈的知识。
其实很简单,FragmentTransaction中提供了一个addToBackStack()方法,可以将一个事务添加到返回栈中。
我们先回顾一下之前动态加载Fragment的代码,然后在此基础之上,增加一行代码就可以将Fragment添加到返回栈中:(即第07行代码)
//步骤一:添加一个FragmentTransaction的实例 FragmentManager fragmentManager =getFragmentManager(); FragmentTransaction transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction(); //步骤二:用add()方法加上Fragment的对象 RightFragment rightFragment = new RightFragment(); transaction.add(R.id.right, rightFragment); transaction.addToBackStack(null); //步骤三:调用commit()方法使得FragmentTransaction实例的改变生效 transaction.commit();
第07行代码:我们在事务提交之前调用了FragmentTransaction的addToBackStack()方法,它可以接受一个名字用于描述返回栈的状态,,一般传入null即可。
【实例】现在通过代码来实现以下界面(下面的图片为程序运行时加载的首页),并且把每一个Fragment都加入到返回栈当中去,然后观察其生命周期的变化。完整代码如下:

首先新建工程文件m01_Fragment04,然后开始我们的代码之旅:
我们先把右侧的四个Fragment建起来吧:
Fragment01.java主要部分的代码如下:
1 package com.example.m01_fragment04;
2
3 import android.app.Fragment;
4 import android.os.Bundle;
5 import android.view.LayoutInflater;
6 import android.view.View;
7 import android.view.ViewGroup;
8
9 public class Fragment01 extends Fragment {
10
11 @Override
12 public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
13 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
14 }
15
16 @Override
17 public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
18 Bundle savedInstanceState) {
19 View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.f1, null);
20 return view;
21 }
22 @Override
23 public void onPause() {
24 super.onPause();
25 }
26 }
为避免啰嗦,这里就不把Fragment01生命周期中的其他函数罗列出来了,我们只要知道在实际代码中这些函数都是加了的。
Fragment01的布局文件f1.xml的代码如下:
< xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" >
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="加载图片" />
</LinearLayout>
然后依次新建出Fragment02、Fragment03、Fragment04的java代码和布局文件。
MainActivity的布局文件activity_main.xml代码如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/left"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#CCCCCC"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="加载图片" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="海报管理" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="照片管理" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="新闻管理" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/right"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical" >
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
其中,第一个LinearLayout表示左侧的按钮,第二个LinearLayout留给右边的Fragment。
MainActivity.java的代码如下:
1 package com.example.m01_fragment04;
2
3 import android.os.Bundle;
4 import android.app.Activity;
5 import android.app.FragmentManager;
6 import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
7 import android.view.Menu;
8 import android.view.View;
9 import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
10 import android.widget.Button;
11
12 public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener{
13
14 private FragmentManager manager;
15 private FragmentTransaction transaction;
16 private Button button1,button2,button3,button4;
17
18 @Override
19 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
20 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
21 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
22
23 manager = getFragmentManager();
24 button1 = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.button1);
25 button1.setOnClickListener(this);
26 button2 = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.button2);
27 button2.setOnClickListener(this);
28 button3 = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.button3);
29 button3.setOnClickListener(this);
30 button4 = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.button4);
31 button4.setOnClickListener(this);
32
33 }
34
35 @Override
36 public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
37 // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
38 getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
39 return true;
40 }
41
42 //通过点击不同的按钮,跳转到不同的Fragment
43 @Override
44 public void onClick(View v) {
45 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
46 transaction = manager.beginTransaction(); 47 switch (v.getId()) {
48 case R.id.button1:
49 Fragment01 fragment01 = new Fragment01();
50 transaction.replace(R.id.right, fragment01, "fragment01");
51 transaction.addToBackStack("fragment01");// 添加到Activity管理的回退栈中。
52 break;
53
54 case R.id.button2:
55 Fragment02 fragment02 = new Fragment02();
56 transaction.replace(R.id.right, fragment02, "fragment02");
57 transaction.addToBackStack("fragment02");// 添加到Activity管理的回退栈中。
58 break;
59
60 case R.id.button3:
61 Fragment03 fragment03 = new Fragment03();
62 transaction.replace(R.id.right, fragment03, "fragment03");
63 transaction.addToBackStack("fragment03");// 添加到Activity管理的回退栈中。
64 break;
65
66 case R.id.button4:
67 Fragment04 fragment04 = new Fragment04();
68 transaction.replace(R.id.right, fragment04, "fragment04");
69 transaction.addToBackStack("fragment04");// 添加到Activity管理的回退栈中。
70 break;
71 }
72 transaction.commit();
73 }
74
75 }
上当代码中,通过点击不同的按钮,就能跳到对应的Fragment,而这四个Fragment都已经加入到了返回栈当中。运行程序之后,也是这样的。
注意第46行和第72行,transaction = manager.beginTransaction()意味着开始,transaction.commit()意味着结束。
我们就其中的fragment01和fragment02来讨论一下他们的生命周期的变化:
运行程序后,界面如下,没有任何fragment被加载:

点击左侧第一个按钮,加载fragment01:

点击左侧第二个按钮,加载fragment02(此时fragment01被替换,并被压到了栈当中):

注:假如fragment01在替换的时候没有被压到栈中,那就会被销毁,在执行完onDestroyView()方法后,会继续执行onDestroy()和onDetach()方法。
按Back键,fragment01重新返回到屏幕:(fragment02被销毁)

再按Back键,fragment01被销毁:

注:Fragment的返回栈由Activity管理;而Activity的返回栈由系统管理。


